Class X: Chapter 4 (Agriculture) Questions & Answers
Q1. Jute is known as an important fiber crop; mention some of its uses.
Ans: Jute is also known as the 'Golden Fiber'. Jute is used to make gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets, etc.
Q2. Write the main characteristics of the Intensive Subsistence Agriculture.
Ans: Following are some of the main characteristics of the Intensive Subsistence Agriculture practiced in India:
(a) This type of farming is practiced in thickly populated areas.
(b) In this activity, farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour.
(c) There is huge population pressure on this type of farming.
(d) It is labour intensive.
(e) In a year 2 to 3 crops are grown.
(f) This involves high degree of use of biochemical inputs and irrigation for obtaining high production.
Q3. Explain the climatic conditions required for rubber cultivation in India.
Ans: Following are some of the climatic conditions required for rubber cultivation in India:
(a) Rubber is a plantation crop.
(b) Rubber is a crop of equatorial region but it is also grown tropical and subtropical regions.
(c) It needs moist and humid climate.
(d) It requires a temperature above 25°C.
(e) Annual rainfall above 200 cm.
(f) Major producers: Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andaman & Nicobar islands and also in the Garo hills of Meghalaya.
(g) India is the fourth largest rubber producer in the world.
Q4. Describe the geographical conditions required for the cultivation of cotton in India.
Ans: Following are the geographical conditions required to grow cotton in India:
(a) Cotton requires high temperature more than 25°C.
(b) It requires light rainfall: 60 – 85 cm annually.
(c) Cotton requires 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine for its growth.
(d) It grows best on the drier parts of black cotton soil and requires at least 6 to 8 months.
(e) Major producers: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
(f) India was the second largest producer of cotton after China.
Q5. Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
Ans: Following are some of the programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers:
(a) Green Revolution
(b) White Revolution
(c) Land Reform
(d) Establishment of Grameen Banks, Cooperative Societies.
(e) Providing loan facilities at lower rates of interest.
(f) Kissan Credit Cards (KCC).
(g) Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers were introduced on radio and television. For e.g. Krishi Darshan.
(h) The Government also introduced "Minimum Support Price, Remunerative and Procurement Prices for important crops" to check the exploitation of farmers by the speculators and middlemen.
Q6. What is plantation cropping? Mention some of the important features of the plantation cropping in India.
Ans: Plantation cropping is a type of commercial farming, where a single crop is grown on a large area. Following are some of the important features of the plantation cropping in India:
(a) More capital and a large number of workers are required.
(b) Final output of the plantation is used in various industries.
(c) Important plantation crops of India are: tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana, etc.
(d) Plantation requires a well developed network of transportation, communication, processing industries and a good market.
Q7. Elaborate the cropping seasons of India.
Ans: India has three cropping seasons, i.e. Rabi, Kharif and Zaid.
(a) Rabi:
(i) Crops are sown in winters between October to December and harvested between April to June.
(ii) Some of the major crops of this season are: wheat, barley, peas, gram, and oilseeds.
(iii) Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are the important producers of rabi crops.
(b) Kharif:
(i) Crops are sown at the beginning of monsoon and harvested after rain i.e. between September to October.
(ii) Kharif crops are also known as summer crops.
(iii) Some of the major crops of this season are: rice, maize, jowar, bajra, jute.
(iv) Orissa, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are important rice growing states.
(v) In Assam, West Bengal and Orissa; three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are called Aus, Aman and Boro.
(c) Zaid:
(i) In between Rabi and Kharif crops zaid crops.
(ii) Some of the major crops of this season are: watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops.
(iii) Sugarcane is planted in this season but takes almost a year to grow.
Q8. Mention the geographical conditions required to grow maize crop in India.
Ans: Maize is used as both food and fodder crop. It is also known as "Corn". Following are the geographical conditions required to grow millet crops in India:
(a) Maize is basically a kharif crop. But in states like Bihar it is grown in rabi season.
(b) It requires a temperature range of 21°-27°C.
(c) Annual rainfall between 50 cm - 100 cm.
(d) It grows best in old alluvial soil,
(e) Major producers: Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
Q9. Highlight the key factors of coffee production in India. Which variety of Indian coffee is well known for its good quality throughout the world?
Ans: Following are the key factors of coffee production in India:
(a) Coffee is a plantation crop.
(b) It is the second most important beverage crop in India.
(c) Hill slopes are more suitable for growth of this crop.
(d) India produced 3.2% of the total world coffee production.
(e) The cultivation of coffee was initially introduced on the Baba Budan Hills.
(f) Major producers: Nilgiris in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Indian coffee is well known for its good quality throughout the world. The Arabica variety of coffee was brought from Yemen and the thereon produced in India.
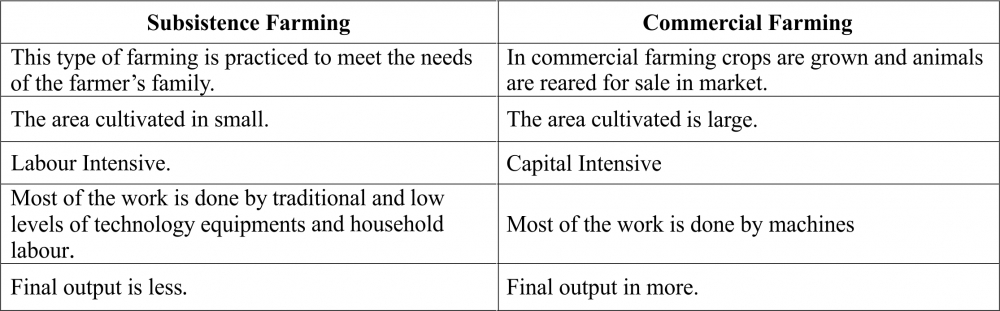
Q10. Differentiate between Subsistence Farming and Commercial Farming.
Ans:
-----x-----X-----x-----

There are no published comments.
New comment