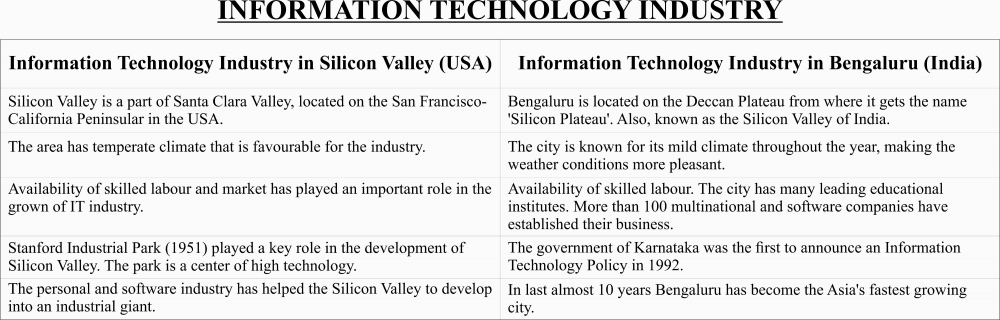
INDUSTRIES - COMPARATIVE STUDY 3

1. Agriculture is:
(a) Primary Activity
(b) Secondary Activity
(c) Tertiary Activity
(d) None of the above
2. Slash and burn practice of agriculture is also known as:
(a) Intensive Farming
(b) Extensive Farming
(c) Shifting Farming
(d) Nomadic Farming
3. Which is also known as golden fiber?
(a) Cotton
(b) Wheat
(c) Silk
(d) Jute
4. The two most important staple food crops of the world are ................... and ..................
(a) Ragi & Bajra
(b) Tea & Coffee
(c) Rice & Wheat
(d) Millets & Maize
5. It is also known as "Monoculture", i.e. single crop grown over a large area.
(a) Commercial Grain Farming
(b) Plantation Farming
(c) Multiple Farming
(d) Mixed Farming
6. Out of the following which is not a cropping season of India?
(a) Zaid
(b) Kharif
(c) Kaffir
(d) Rabi
7. Which one is not a millet crop?
(a) Jowar
(b) Ragi
(c) Wheat
(d) Bajra
8. The type of agriculture practiced in India is:
(a) Intensive Farming
(b) Extensive Farming
(c) Primitive Farming
(d) Mixed Farming
9. The word "Agriculture" has been derived from two ...................... Words.
(a) German
(b) American
(c) Latin
(d) Arabic
10. Cultivation of grapes is also known as ..................
(a) Viticulture
(b) Horticulture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Pisciculture
11. Seasonal migration of people with their animals is called
(a) Farmers
(b) Jhumming
(c) Transhumance
(d) Labours
12. Classification of Commercial farming (which is not correct)
(a) Commercial Grain Farming
(b) Plantation Farming
(c) Multiple Farming
(d) Mixed Farming
13. Factors Influencing the Crop Cultivation:
(a) Temperature
(b) Fertile Soil
(c) Rainfall
(d) All of these
14. Growing vegetables, flowers, fruits and decorative plants for commercial use is known as
(a) Viticulture
(b) Horticulture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Pisciculture
15. ...................... is grown in winter. It requires rainfall during growing season and bright sunshine at the time of harvest.
(a) Rice
(b) Watermelon
(c) Wheat
(d) Bajra
16. The land on which crops are grown is known as
(a) Arable Land
(b) Wet Land
(c) Dry Land
(d) None of these
17. Jhumming, Ladang, Milap, Roca & Ray are also known as
(a) Intensive Farming
(b) Commercial Farming
(c) Nomadic Farming
(d) Shifting Farming
18. .................... requires high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine.
(a) Jute
(b) Cotton
(c) Tea
(d) Coffee
19. In .............. farming the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
(a) Intensive Farming
(b) Plantation Farming
(c) Primitive Farming
(d) Mixed Farming
20. Tea is a ...................... crop
(a) Fiber Crop
(b) Food Crop
(c) Beverage Crop
(d) Industrial Crop
-----x-----X-----x-----
Q1. Define: (a) Jhumming (b) Transhumance (c) Arable Land
Ans: (a) Jhumming: Shifting agriculture in India is known as Jhumming.
(b) Transhumance: The seasonal movement with livestock, uphill during the summers and downhill during the winters in search of pastures is called Transhumance.
(c) Arable Land: The land on which crops are grown is known as "Arable Land.
Q2. What is Agriculture?
Ans: The science and art of cultivation on the soil, raising crops and rearing livestock. It is also called farming. The word "Agriculture" has been derived from the Latin word "Ager or Agri" meaning "Soil" and "Culture" means "Cultivation".
Q3. What are the factors affecting Agriculture?
Ans: Some of the physical and economic factors which greatly influence agriculture are:
Physical Factors: Relief, Climatic Conditions (Temperature, Rainfall, etc.), Fertility of Soil, etc.
Economic Factors: Availability of farm inputs (Capital, Good quality seeds, Fertilizers, Tools & Machines, etc.), Availability of cheap labour, Transportation Facility, Market, Government Policies, etc.
Q4. What is a farm system?
Ans: Agriculture or farming can be looked at as a system.
(a) Input: The important inputs are seeds, fertilisers, machinery, labour, etc.
(b) Process: Some of the operations involved are ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding & harvesting.
(c) Output: The outputs from the system include crops, wool, dairy, poultry products, etc.
Q5. Define types of economic activities.
Ans: There are three types of economic activities. These are:
(a) Primary Activities: Connected with extraction and production of natural resources like forestry, agriculture, mining, animal husbandry, etc.
(b) Secondary Activities: Connected with processing and manufacturing of primary goods into finished goods. They get raw material from the Primary sector. For e.g. Iron ore into tools & machines, sugar cane into sugar, etc.
(c) Tertiary Activities: Provides support to Primary and Secondary sectors through services, e.g. transportation, banking, tourism, etc.
Q6. Write a short note explaining the different cropping seasons.
Ans: There are three major cropping seasons, i.e. Rabi, Kharif and Zaid.
(a) Rabi: Crops are sown in winters between October to December and harvested between February to April. Major crops of this season are: wheat, barley, peas, gram, and oilseeds.
(b) Kharif: Crops are sown in summers between May to July and harvested after rain i.e. between September to October. Major crops of this season are: rice, maize, jowar, bajra, sugarcane, jute.
(c) Zaid: In between Rabi and Kharif crops zaid crops like: watermelon, cucumber are grown between April to June.
Q7. What is Agriculture Development?
Ans: Agricultural Development refers to efforts made to increase farm production in order to meet the growing demand of increasing population. This can be achieved in many ways such as:
(a) Increasing the cropped area.
(b) Multiple cropping (Number of crops grown in a year)
(c) Improving irrigation facilities
(d) Use of fertilizers and high yielding variety of seeds.
(e) Mechanization of agriculture is also another aspect of agricultural development.
Q8. What are Millets? List out the geographical conditions required for the cultivation of millets.
Ans: Millets are a group of highly variable small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as grains. Millets are also known as coarse grains. Geographical conditions required for the cultivation of millets are:
(a) These grains can be grown on less fertile and sandy soils.
(b) It needs low rainfall and high to moderate temperature.
(c) Jowar, bajra and ragi are millet crops grown in India.
(d) Major producers: China, India, Nigeria, USA, Brazil, etc.
Q9. State the geographical conditions favourable for cultivation of:
(a) Rice (b) Wheat (c) Cotton (d) Coffee
Ans: Following are the geographical conditions required for the cultivation of rice and wheat:-
(a) Rice:
• Rice is the major food crop of the world. It is the staple diet of the tropical and sub-tropical regions.
• Rice needs high temperature, high humidity and rainfall. It grows best in alluvial clayey soil, which can retain water.
• Leading producers of rice in the world: - China, India, Japan, Sri Lanka, etc.
(b) Wheat:
• It requires moderate temperature and rainfall during growing season and bright sunshine at the time of harvest.
• It requires well drained loamy soil for its growth.
• Wheat is grown extensively in USA, Canada, Argentina, Russia, Ukraine, Australia and India.
(c) Cotton:
• Cotton is a fiber crop grown in tropical areas. Cotton requires high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine for its growth.
• It grows best on black soil and requires at least 6 to 8 months.
• China, USA, India, Pakistan, Brazil and Egypt are the leading producers of cotton. It is one of the main raw materials for the cotton textile industry.
(d) Coffee:
• Hill slopes are more suitable for growth of this crop.
• It requires warm & wet climate and well drained loamy soil.
• Brazil is the leading producer followed by Columbia and India.
• In India coffee is cultivated in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
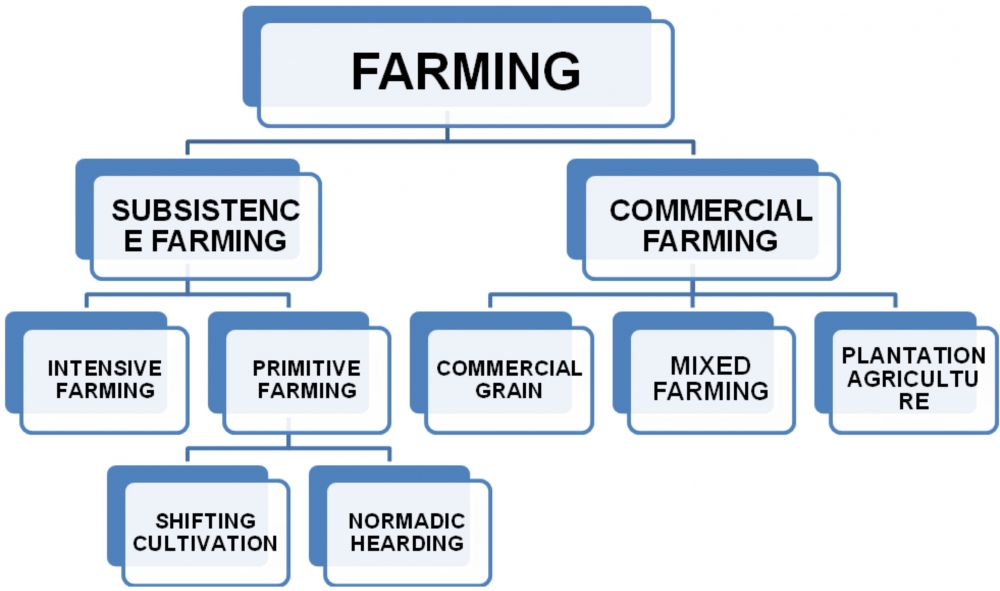
Q10. Explain subsistence farming and Commercial farming. Draw a flow chart to define types of Farming.
Ans:
(a) Subsistence Farming: This type of farming is practiced to meet the needs of the farmer's family. Traditionally, low levels of technology and household labour were used to produce on small output. Subsistence farming can be further classified as intensive and primitive farming.
Primitive farming is further classified into two: Shifting cultivation and Nomadic herding.
(b) Commercial Farming: In commercial farming crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in market. The area cultivated and the amount of capital used is large. Most of the work is done by machines. Chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides and high yielding variety of seeds are used in order to get maximum output.
Commercial farming includes commercial grain farming, mixed farming and plantation agriculture.
-----x-----X-----x-----
CHAPTER - 1 (INDIA - SIZE & LOCATION)
Tropic of Cancer, Standard Meridian of India, Southern most point of India, Southernmost point of Indian mainland, Northernmost point of India, Easternmost meridian of India, Westernmost Meridian of India.
CHAPTER - 2 (PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA)
(a) Mt. Peaks: Mt. Everest, K2, Kanchenjunga, Nanda Devi, Anai Mudi, Mahendra Giri.
(b) Passes: Bomdi-la, Nathula, Shipkila.
(c) Hills: Garo, Khasi, Jaintia, Naga hills, Mizo hills.
(d) Mountain Ranges: The Karakoram, Zaskar, Shivaliks, Aravalli, Vindhya, Satpura, Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats.
(e) Plateaus: Deccan plateau, Chota Nagpur plateau, Malwa plateau.
(f) Coastal Strips: Coromandel, Northern Circar, Malabar, Konkan.
CHAPTER - 3 (DRAINAGE)
(a) Lakes: Chilka, Pulicat, Kolleru, Sambhar, Wular.
(b) Rivers: Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, Satluj, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri.
-----x-----X-----x-----
CHAPTER – 1 (INDIA- SIZE AND LOCATION)
Q1. Describe the location and size of India.
Q2. Why is the difference between the duration of the day and night hardly felt in Kanyakumari but it is not so in Kashmir?
Q3. Distinguish between latitudes and Longitude.
Q4. How does India occupy an important strategic position in South Asia? Illustrate your answer by explaining three suitable points.
Q5. Which latitude and longitude divides India into two halves?
Q6. What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India in degrees?
Q7. Name the canal that shortened the distance between India and Europe.
Q8. Why 82o30' East longitude (Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh) is taken as the Standard Time Meridian of India?
Q9. Name the countries which are larger than India.
Q10. Name the two countries which are our southern neighbors.
Q11. Name the southernmost latitude of Indian Territory, which got submerged in the year 2004. Also, write its degree.
CHAPTER 2 (PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA)
Q1. Mention the nature of geology and topography of the Himalayas, the Peninsular Plateau and the Northern Plains.
Q2. Why Himalayas are called the young fold mountains?
Q3. Pitti Island is located in Lakshadweep islands. Write any two features of the Pitti island.
Q4. Which island was earlier known as Laccadive, Minicoy and Amindive.
Q5. India's only active volcano is located in which part of the Andaman and Nicobar islands?
Q6. Write three important features of the Indian Desert.
Q7. What is Doab?
Q8. The Deccan Plateau extends towards the east, name the three prominent hill ranges from west to east.
Q9. Which are the two landforms that have developed most recently?
Q10. Write any five characteristics of the Great Himalayas.
Q11. Write any five characteristics of the Peninsular Plateaus.
Q12. Write any five characteristics of the Northern Plains.
Q13. Mention five characteristics of the Eastern Himalayas.
Q14. What are Duns? Give some examples.
Q15. Name the divisions of the Western Coastal Plains.
Q16. Name the divisions of the Eastern Coastal Plains.
Q17. Name the three types of plate boundaries. Write one characteristic each.
Q18. Name the three types of stress built with the plates, with a suitable example.
Q19. Write three important features of the Aravalli hills.
Q20. Name the three major divisions of the Himalayas from north to south.
Q21. Name the four major divisions of the Himalayas from west to east.
Q22. Name the group of islands having the coral origin.
CHAPTER – 3 (DRAINAGE)
Q1. Explain the formation of fresh water lake in the Himalayan region. Give an example.
Q2. Why rivers are considered lifelines of the human civilizations. Explain any three reasons.
Q3. What progress has been made in the Ganga Action Plan?
Q4. What are the major factors responsible for river pollution? Explain.
Q5. Mention any three features of Indian Drainage System.
Q6. What is the importance of lakes? or How lakes are of great value to human beings? State any five importance. or Mention some characteristics of lakes.
Q7. How does a river affect the economy of a country?
Q8. From where does the river Brahmaputra rise? Name the two tributaries of the river Brahmaputra.
Q9. In which two groups are the Indian rivers divided? Write four points to differentiate between the two.
Q10. Name the largest riverine island made by the Brahmaputra River.
Q11. Name the major tributaries of river Indus.
Q12. What are the major factors responsible for reducing the volume of water in Indian rivers?
Q13. Explain the "National River Conservation Plan" in brief.
Q14. Write five important features of the Ganga river system.
Q15. Mention a short note on the Godavari river system.
Q16. Write a note on the Peninsular Rivers.
Q17. Explain the different drainage patterns formed by the rivers.
-----x-----X-----x-----
1.What was the main object of National Assembly in France while drafting the constitution in 1791?
2. Which drainage pattern is formed by River Ganga?
3 .Which is the western most longitude of India?
4. Name the part of Himalaya lying between Kali and Tista rivers.
5. Pinochet rule in Chile ended after he decided to hold a referendum. In which year was referendum held?
6. When did Mexico get independence?
7.How much time did it take the Constituent Assembly to complete the Indian Constitution?
8 .What was the expenditure percentage of GDP in 1951-52 on education?
9. Describe the events of 14th July 1789.
10 (a) Who were radicals? Describe briefly.
OR
10 (b) Explain the new education policy introduced by Hitler in Germany.
11 (a) Explain any three differences between the political ideas of Liberals and Radicals in Russia during the early twentieth century.
OR
11(b) Highlight three main features of the Nazi World view?
12. India accounts for about 2.4 percent of the total geographical area of the world but supports the second largest population of the world. What are its three implications?
13. Justify the naming of Indian Ocean after India.
14. Mention any six tectonics plates of the earth's crust.
15. Name the three sections into which Northern plain has been divided. Write one feature of each.
16. How did Robert Mugabe's party ZANU PF violate the features of a democratically elected government? Mention any three methods adopted by the party.
17. ‟The Constituent Assembly worked in a systematic open and consensual manner." Mention any three values that are depicted by the Constituent Assembly.
18. Describe any three demands of the workers of "Lenin Shipyard" during their strike which started in August 1980 in Poland.
19. Describe any three ways by which production can be increased from a fixed plot of land.
20. What does a "virtuous cycle" created by the educated parents mean? Explain.
21. Explain the immediate causes of the outbreak of the revolt in France in 1789.
22 (a) Explain any five socio –economic conditions of Russia at the beginning of the twentieth century?
OR
22 (b) Hitler's foreign policy aimed at gaining power and prestige for Germany. State this features of his foreign policy.
23. Give an account of the four divisions of Himalayas from west to east along with Purvanchal hills respectively.
24. Even democracy has a fair share of demerits. Point out five such demerits.
25. Highlight the salient features of the Constitution of India.
26. Explain the meaning of "Physical Capital"? Explain its two types with the help of suitable examples.
27. Explain any five effects of unemployment in India.
28. "Green Revolution is associated with loss of soil fertility". In the light of the statement mention five problems caused by modern farming.
29. Three items A, B and C are shown in the given outline map of France. Identify these items with the help of following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
(A) Port related to slave trade.
(B) The region not affected by the great fear.
(C) The place where French revolution of 1789 started.

30. On the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols:
(X) Standard Meridian of India
(Y) Jaintia Hills
(Z) River Tapi
_1_o.jpg)
-----x-----X-----x-----