Class VIII: Chapter 3 (Mineral and Power Resources) Question & Answers
Q1. Define minerals.
Ans: A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is known as a mineral.
Q2. Name the leading producers of petroleum in the world.
Ans: The leading producers of petroleum in the world are Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Qatar. The other major producers are USA, Russia, Venezuela, and Algeria.
The leading producers in India are Digboi in Assam, Bombay High in Mumbai and the deltas of Krishna and Godavari rivers.
Q3. What are the main characteristics of minerals?
Ans: The three main characteristics of minerals are:
(a) Minerals are present in impure form and it takes millions of year to form these minerals.
(b) Minerals are unevenly distributed throughout the world.
(c) Minerals are non-renewable 'exhaustible' resources.
Q4. Mention the distribution of minerals in North America.
Ans: The mineral deposits in North America are located in three zones:
(a) Canadian Shield - Iron ore, Nickel, Gold, Uranium and Copper.
(b) Appalachian Region – Coal
(c) Western Cordilleras - Copper, Lead, Zinc, Gold and Silver.
Q5. Why minerals are considered as an important asset to mankind?
Ans: Minerals are considered as an important asset to mankind, because of the following reasons:
(a) Backbone of Industries.
(b) Necessary for the production of all types of tools, machines, implements, etc.
(c) Construction Work.
(d) Maintain health of the people.
(e) Manufacturing of jewellery, utensils, etc.
Q6. Explain the methods of mineral extraction.
Ans: Minerals can be extracted by Mining, Drilling and Quarrying.
(a) Mining: The process of taking out minerals from rocks buried under the earth's surface is called mining.
(i) Open Cast Mining: Minerals that lie at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer is known as "Open Cast Mining".
(ii) Shaft Mining: Deep bores, called shafts, have to be made to reach mineral deposits that lie at great depth; this is known as "Shaft Mining".
(b) Drilling: Petroleum and natural gas occur far below the earth's surface. Deep wells are bored to take them out; this is called "Drilling".
(c) Quarrying: Minerals that lie near the earth's surface are simply dug out by the process known as "Quarrying".
Q7. How can we conserve minerals and power minerals?
Ans: Population growth, urbanization and industrialization have increased the consumption of minerals and power minerals to a greatest extent in the 21st century and there is a serious need for the conservation of minerals. Following are the different ways of conserving minerals:
(a) We can make use of energy efficient equipments.
(b) Looking for alternative sources of energy.
(c) Recycling of minerals.
(d) Optimum utilization of minerals.
(e) Improvement in the techniques of extraction and purification of minerals.
Q8. Write a note on the distribution of minerals in India: (a) Iron (b) Bauxite (c) Mica
Ans:
(a) Iron: India has deposits of high grade iron ore. The mineral is found mainly in Jharkhand, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Maharashtra and Karnataka. All other industries depend on iron & steel industry.
(b) Bauxite: Aluminum is obtained from bauxite. Major bauxite producing areas are Jharkhand, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Telangana and Tamil Nadu. Aluminum has strength of iron, but it is extremely light.
(c) Mica: Mica deposits mainly occur in Jharkhand, Bihar, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan. India is the largest producer and exporter of mica in the world. Mica is made up of series of plates or leaves. It is used in Electric & Electronic industries. Mica can be of black, green, red, yellow or brown is colour.
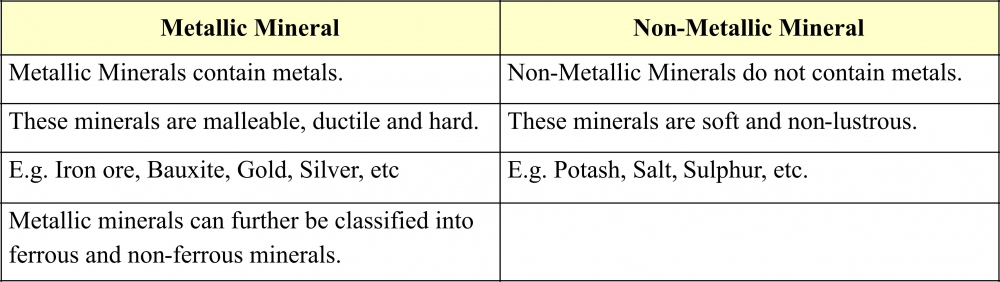
Q9. Distinguish between Metallic and Non-Metallic minerals.
Ans:
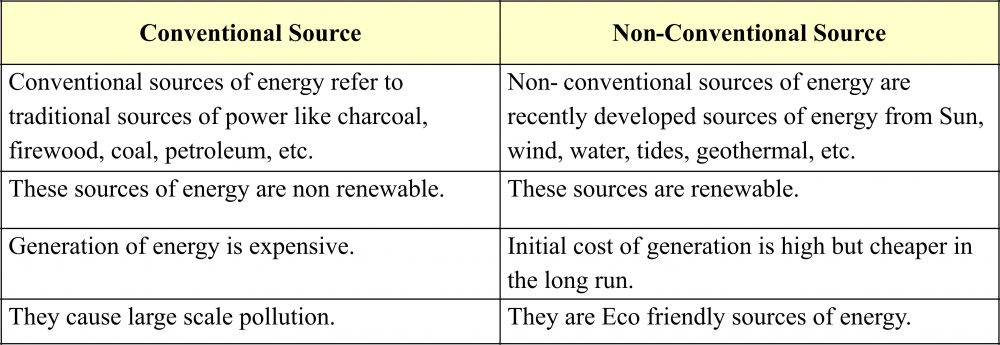
Q10. Distinguish between Conventional and non-conventional power resources.
Ans:
Q11. Explain the different types of minerals on the basis of their composition.
Ans: Minerals are broadly classified into three types: Metallic, Non-Metallic and Power Minerals.
(a) Metallic Minerals: Most of the metallic minerals are found in old plateaus which mainly contains igneous and metamorphic rocks. E.g. Iron, Nickel, Platinum, etc. Metallic minerals are further classified into: Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Minerals.
(i) Ferrous Minerals: These minerals contain iron, for e.g. iron, nickel, etc.
(ii) Non-Ferrous Minerals: These minerals do not contain iron, for e.g. gold, silver, etc.
(b) Non-Metallic Minerals: These minerals are found in the young fold mountains, which mainly consist of sedimentary rocks. E.g. Limestone, Sandstone, Marble, etc.
(c) Power Minerals: Power or energy minerals play a vital role in our lives. We also need power for industry, agriculture, transport, communication and defense. Power resources may be broadly categorized as conventional and non-conventional resources.
(i) Conventional Resources: These resources have been used for a very long time. For e.g. Firewood, cattle dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas, etc.
(ii) Non-Conventional Resources: These resources are called new sources of energy. For e.g. Solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas, etc.
Q12. Write a note on: (a) The Geothermal Energy (b) The Solar Energy
Ans: (a) The Geothermal Energy: Heat energy obtained from the earth is called geothermal energy. The temperature in the interior of the earth rises steadily as we go deeper. Sometimes this heat energy may surface itself in the form of hot springs. This heat energy can be used to generate power. Geothermal energy in the form of hot springs has been used for cooking, heating and bathing, etc.
USA has the world's largest geothermal power plants followed by New Zealand, Iceland, Philippines and Central America.
In India, geothermal plants are located in Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh and Puga Valley in Ladakh.
(b) The Solar Energy: Solar energy trapped from the sun can be used in solar cells to produce electricity. Many of these cells are joined into solar panels to generate power for heating and lighting purpose. The technology of utilizing solar energy benefits a lot of tropical countries that are blessed with abundant sun shine. Solar energy is also used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers besides being used for community lighting and traffic signals.
The largest solar plant of India is located at Madhapur near Bhuj (Gujarat).
-----x-----X-----x-----