Class VIII: Chapter 5 (Agriculture) Question and Answers
Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define: (a) Jhumming (b) Transhumance (c) Arable Land
Ans:
(a) Jhumming: Shifting agriculture in India is known as Jhumming.
(b) Transhumance: The seasonal movement with livestock, uphill during the summers and downhill during the winters in search of pastures is called Transhumance.
(c) Arable Land: The land on which crops are grown is known as "Arable Land.
Q2. Define: (a) Sericulture (b) Pisciculture (c) Viticulture (d) Horticulture
Ans:
(a) Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to obtain silk on a large scale.
(b) Pisciculture: Rearing of fishes on a large scale.
(c) Viticulture: Cultivation of grapes.
(d) Horticulture: Growing vegetables, flowers, fruits and decorative plants for commercial use.
Q3. What is Agriculture?
Ans: The science and art of cultivation on the soil, raising crops and rearing livestock. It is also called farming.
The word "Agriculture" has been derived from the Latin word "Ager or Agri" meaning "Soil" and "Culture" means "Cultivation".
Q4. What is the factors affecting Agriculture?
Ans: Some of the physical and economic factors which greatly influence agriculture are:
Physical Factors: Relief, Climatic Conditions (Temperature, Rainfall, etc.), Fertility of Soil, etc.
Economic Factors: Availability of farm inputs (Capital, Good quality seeds, Fertilizers, Tools & Machines, etc.), Availability of cheap labour, Transportation Facility, Market, Government Policies, etc.
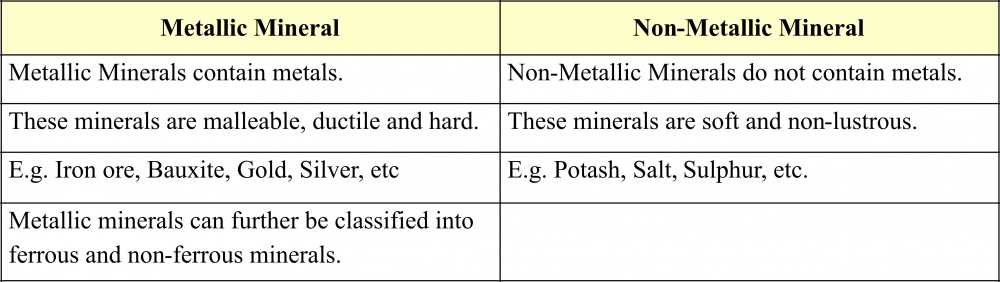
Q5. Differentiate between primary and secondary activities?
Ans:
Long Answer Questions
Q6. Explain: Types of Farming with the help of a flow chart.
Ans. Farming is practiced in various ways across the world. Depending upon the geographical conditions, demand of produce, labour and level of technology, farming can be classified into following types: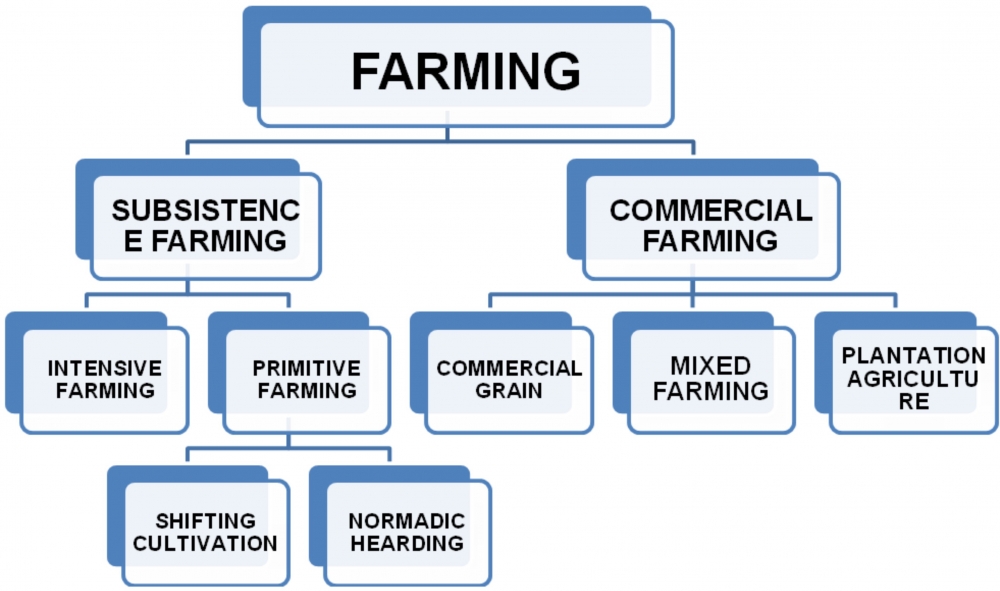
SUBSISTENCE FARMING
This type of farming is practiced to meet the needs of the farmer's family. Traditionally, low levels of technology and household labour were used to produce on small output. Subsistence farming can be further classified as intensive subsistence and primitive subsistence farming.
1. Intensive Subsistence Agriculture:
• In intensive subsistence agriculture the farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour.
• Climate with large number of days with sunshine and fertile soils permit growing of more than one crop annually on the same plot.
• Rice is the main crop. Other crops include wheat, maize, pulses and oilseeds.
• Intensive subsistence agriculture is practiced in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, southeast and east Asia.
2. Primitive Subsistence Agriculture:
(a) Shifting Cultivation:
• Shifting cultivation is practiced in the thickly forested areas of Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of Southeast Asia and Northeast India. These are the areas of heavy rainfall and quick regeneration of vegetation.
• A plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with the soil and crops like maize, yam, potatoes and cassava are grown. When soil loses its fertility, the land is abandoned and the cultivator moves to a new plot.
• Shifting cultivation is also known as 'slash and burn' agriculture.
• It is known by different names in the world – Jhuming in North-Eastern States of India, Milpa in Mexico, Roca in Brazil, Ladang in Malaysia and Ray in Vietnam.
(b) Nomadic Herding:
• Nomadic herding is practiced in the semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia and some parts of India, like Rajasthan and Jammu and Kashmir.
• In this type of farming, Herder does not grow any fodder but move from one place to another with their animals for fodder and water, along defined routes.
• Sheep, Camel, Yak and Goats are most commonly reared. They provide milk, meat, wool and other products to the herders and their families.
COMMERCIAL FARMING
In commercial farming crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in market. The area cultivated and the amount of capital used is large. Most of the work is done by machines. Chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides and high yielding variety of seeds are used in order to get maximum output.
Commercial farming includes commercial grain farming, mixed farming and plantation agriculture.
1. Commercial Grain Farming:
• Crops are grown for commercial purpose.
• Wheat and maize are common commercially grown crops.
• Major areas where commercial grain farming is practiced are temperate grasslands of North America, Europe and Asia. These areas are thinly populated with large farms spreading over hundreds of hectares.
• Severe winters restrict the growing season and only a single crop can be grown.
2. Mixed Farming:
• In mixed farming the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
• It is practiced in Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, southeast Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
3. Plantations:
• It is also known as "Monoculture", i.e. single crop grown over a large area.
• Plantations are a type of commercial farming where single crop of tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton are grown.
• Large amount of labour and capital are required.
• The produce may be processed on the farm itself or in nearby factories.
• The development of a transport network is thus essential for such farming.
• Major plantations are found in the tropical regions of the world. Rubber in Malaysia, coffee in Brazil, tea in India and Sri Lanka are some examples.
-----x-----X-----x-----

_2_o.jpg) DIWALI
DIWALI
_0_o.jpg)