
 3_1_o.jpg)

 3_1_o.jpg)
Q1. What is a lake? How are lakes formed?
Q2. What is water pollution? Write its main sources of water pollution in Indian Rivers.
Q3. Mention 5 features of GAP1 and GAP2.
Q4. Why are lakes and rivers important for countries economy?
Q5. With the help of stable diagram explain drainage patterns.
Q6. Why rivers are considered lifelines of human civilizations? Explain any 3 reasons.
Q7. Discuss significant differences between Himalayan and Peninsular rivers.
Q8. Compare east flowing and west flowing rivers of peninsular plateau.
Q9. Write about the following:
(a) Water divide.
(b) River System.
(c) River Godavari.
Q10. Explain about the following:
(a) River Ganga.
(b) River Indus.
(c) River Brahmaputra.
Q11. Map Skills:
(i) On an outline map of India mark and label the following rivers: Ganga, Satluj, Damodar, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, and Brahmaputra.
(ii) On an outline map of India mark and label the following lakes: Chilika, Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat, Kolleru.
-----x-----X-----x-----
Q1. How were Himalayas formed?
Q2. Give any 5 differences between Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats.
Q3. Give 5 main characteristics of Northern Plains.
Q4. Give a brief description of peninsular plateau. Name its sub division.
Q5. Write any 5 characteristics of Indian desert.
Q6. Name 3 parallel ranges of Himalaya. What are their distinguishing features?
Q7. How the plate boundaries are formed? Explain.
Q8. Write a note on Indian island.
Q9. Give 3 ways in which Himalayas are as a boon for India?
Q10. Explain the following:
(a) Purwanchal Hills
(b) Central Highlands
(c) Khadar, Bhangar, Bhabhar and Terai.
-----x-----X-----x-----
Write three examples of each of the following
Q1. Trees found in equatorial forest.
Ans: Trees found in equatorial forest are Rosewood, Ebony, and Mahogany.
Q2. Trees found in taiga forest.
Ans: Trees found in taiga forest are Douglas-Fir, Larch and Redwood.
Q3. Animals found in Africa.
Ans: Animals found in Africa are Elephants, Zebras and Camels.
Q4. Animals found in Europe.
Ans: Animals found in Europe are Polar Bears, Minks and Sables.
Short Answer Questions
Q5. What are the main characteristics of coniferous forest?
Ans: Following are the main characteristics of coniferous forest:
• Limited species of trees are found. These trees are evergreen and grow apart from each other.
• Trees are conical shaped with needle shaped leaves and trees are found in large groups.
• Chir, pine, cedar are the important variety of trees in these forests. Lumbering is the common activity. Soft wood is used for manufacturing paper.
• Fur-bearing animals like Silver fox, mink, and polar bear are the common animals found here.
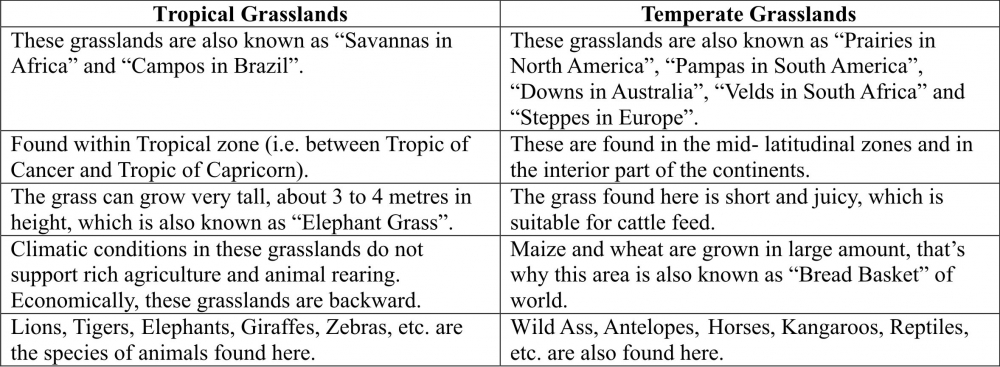
Q6. Distinguish between tropical and temperate grasslands.
Ans:
Q7. Explain the effects of clearance and destruction of natural vegetation.
Ans: The clearance and destruction of natural vegetation has led to major environmental issues. Following are its effects:
(a) Global warming.
(b) Decrease in rainfall.
(c) Soil erosion on a very large scale.
(d) Decrease in underground water.
(e) Decrease in wildlife, as their habitats are destroyed.
(f) Decrease in tribal population, as their habitats are destroyed. Etc.
Q8. What are the role of CITES in saving the flora and fauna?
Ans: CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) is an international agreement between governments. Its aim is to ensure that international trade in products of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival.
Long Answer Questions
Q9. Define – natural vegetation, Wildlife, Ecosystem, Taiga and Deforestation.
Ans:
(a) Natural Vegetation: Natural vegetation refers to a plant community which has grown naturally without human aid and has been left undisturbed by humans for a long time.
(b) Wildlife: Animals living in their natural habitat and not within the possession or control of humans.
(c) Ecosystem: Interrelation between plants and animals in the natural environment is called Ecosystem.
(d) Taiga: coniferous forests are also called "Taiga Forest". This forest belt extends from 50oN and 70oN latitudes. Trees found here are conical shaped with needle shaped leaves.
(e) Deforestation: Deforestation is the cutting down of trees on a large scale from an area with no intention of replanting the trees. Deforestation is one of the main cause of environmental disorder.
Q10. Describe the natural vegetation in hot and cold deserts.
Ans:
(a) Hot Deserts: Natural vegetations found in hot deserts have thick & spongy stems, long roots, wax coated leaves, thorns, etc. Cactus, thorny bushes and coarse grass are main type of vegetation found here. At some places palm trees can be found surrounding the Oasis.
(b) Cold Deserts: In these deserts trees are not found; as trees don't grow below 10° C. Very less vegetation is found. Mosses, Lichens and some shrubs grow here. At some places meadows (short grass cover ground) can also be found.
Q11. Name the typical wildlife found in each continent.
Ans: Some of the typical wildlife found in continents are:
(a) Africa: Elephants, crocodiles, zebras, leopards, camels and ostriches.
(b) Antarctica: Penguins, snow petrels, seals and albatrosses.
(c) Asia: Monkeys, sloths, lynxes and minks.
(d) Australia: Kangaroos, koalas and kookaburras.
(e) Europe: Polar bears, minks, sables and ermines.
(f) North America: Reindeer, arctic foxes, bisons and beavers.
(g) South America: Rheas, condors, anteaters, llamas and anacondas.
Q12. What are the initiatives taken to conserve natural vegetation and wildlife?
Ans: Following are few steps that have been taken to conserve forest and wildlife:
(a) National Forest Policy framed by the government should be implemented.
(b) National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, Bioreserves, Botanical Gardens have been setup.
(c) Special Projects (E.g. Project Tiger, Project Elephant, etc.).
(d) Celebration of Van Mahotsav.
(e) Every National festival is followed by tree plantation ceremony.
(f) Large scale afforestation or planting of tress is undertaken.
(g) Controlling of deforestation and overgrazing.
(h) Practices like shifting agriculture have been stopped.
(i) Social Awareness Programmes to be implemented.
(j) Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
-----x-----X-----x-----

Short Answer Questions
Q1. What is land use? List the factors which control the utilization of land.
Ans1: Land is utilized by human beings for various purposes, for e.g. agriculture, settlement, mining, setting up of industries, etc. such utilization of land is known as Land Use.
Factors affecting the land use pattern of an area are:
(a) Physical Factors: Climate, Topography, Water availability, Soil, Minerals, etc.
(b) Human Factors: Population Density, Need & Desire of People, Development of Technology, etc.
(c) Economic Factors: Cost of living, Occupation, Financial conditions, etc
Q2. What are soil horizons? Explain the various soil horizons present in a soil profile.
Ans2: Vertical section of the soil from the surface to the Bed rock is known as Soil profile. The soil profile is horizontally divided into four different horizons or layers known as Soil Horizons (as shown in the diagram). Top Soil, Sub Soil, Weathered Rock and Bed Rock or Parent Rock.
(a) Top Soil: It is the uppermost layer. Rich in humus and minerals. Consists of Sand, Silt & Clay. Leaching of soil is common in this layer.
(b) Sub Soil: It lies below the top soil and supports moisture. Consists of some amount of weathered rock, Silt & Clay and some nutrients. Minerals found here is more than Horizon A.
(c) Weathered Rock: Consists of large amount of weathered rock. These rocks are not affected by biological processes.
(d) Bed Rock: Last layer of the soil horizon. Consists of solid layer of unweathered Rock.
Q3. Discuss the agricultural practices that can be adopted for soil conservation.
Ans3: Some of agricultural practices that can be adopted for soil conservation are: Mulching, Contour Ploughing, Terrace Cultivation, Strip Cropping, Shelter Belts, Rock Dam, Contour Barriers, Crop Rotation, etc.
Q4. What are the factors responsible for the shortage of freshwater?
Ans4: Due to overpopulation, industrialization and urbanization, the consumption of water has increased manifold. Increased agricultural production to meet the growing needs of the population, modern lifestyle of the people and greater use of electricity in industries has resulted in water scarcity in many parts of the world. Above all the pollution of water bodies is due to irresponsible and reckless attitude of mankind. This has reduced the availability of fresh water for human consumption.
Long Answer Questions
Q5. How can we conserve land resources?
Ans5: Land is a very important resource to the man kind but day-by-day our land is getting degraded. Some of the measures that can be used or practiced to conserve our land resource are:
(a) Adopting to the scientific techniques.
(b) Land Reclamation.
(c) Regulated use of chemical fertilizers, insecticides and pesticides.
(d) Afforestation.
(e) Check on Overgrazing.
(f) Control of Mining Activities.
(g) Proper irrigation facilities.
(h) Constructing retention walls in the mountain areas to stop landslides.
Q6. Write a short note on the soils of India.
Ans6: Soils are of various types depending on their colour, texture, mineral content, fertility level, etc. Different types of soils found in India are:
(a) Alluvial Soil:
• It is the most important and most fertile type of soil found in India.
• Soil is formed by the deposition of sediments brought down by the rivers.
• The alluvial soil is found mostly in the Northern Plains and Coastal Plains of India.
(b) Black Soil:
• The black soil is also called the Black Cotton Soil or Black Lava Soil.
• Cotton grows best in this soil.
• Black soil is formed from the weathering of the igneous rocks.
• The black soil is mostly found in the Deccan Trap, covering large areas of Maharashtra, Gujarat and western Madhya Pradesh.
(c) Red Soil:
• Red soil is derived from the weathering of the igneous and metamorphic rocks.
• The red colour is due to the high percentage of iron contents.
• Red soil is found in the southern and eastern parts of the peninsular plateau.
(d) Laterite Soil:
• The laterite soil is formed when heavy rains wash the fertile upper part of the soil.
• This soil is less fertile.
• Soil is mainly found on the summits of the Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, etc.
(e) Mountain Soil:
• The mountain soil is generally found on the hill slopes covered with forests.
• This type of soil is found in the Himalayan region, the Western and Eastern Ghats and in some parts of the Peninsular India.
• This soil is especially suitable for producing plantation crops, such as tea, coffee.
(f) Desert Soil:
• The desert soil is found mostly in the arid and semi-arid regions.
• This type of soil is found in Rajasthan, parts of Haryana, Gujarat, etc.
• The desert soil is mainly composed of sand.
Q7. Discuss any four methods of soil conservation.
Ans 7: Some methods of soil conservation are:
(a) Mulching – Bare ground between plants is covered with a layer of organic matter like straw. It helps to retail soil moisture.
(b) Contour Ploughing – Ploughing along contours can decrease the flow of water down the slopes.
(c) Terrace Cultivation – Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces.
(d) Strip Cropping – Strips of grass are grown between the crops. This breaks the force of wind.
(e) Shelter Belts – Rows of trees are planted to create shelter. Thus, the speed of wind is reduced.
(f) Rock Dam – Rocks are piled to slow the speed of wind.
(g) Contour Barriers – Stones, grass and soil are used to make barriers. Trenches are made in front of the barriers to collect water.
(h) Afforestation, Crop Rotation, Control over Deforestation and Overgrazing, etc.
Q8. Explain the different methods to conserve water resource.
Ans 8: Some of the important ways to conserve water are:
(a) Decrease of water pollution
(b) Proper irrigation method: Sprinklers and Drip irrigation can be used.
(c) Water Harvesting Method
(d) Water conservation in the home:
• Check faucets and pipes for leaks.
• Check your toilets for leaks.
• Use your water meter to check for hidden water leaks.
• Install water-saving shower heads and low-flow faucet aerators.
• Put plastic bottles or float booster in your toilet tank.
• Insulate your water pipes.
• Take shorter showers.
• Turn off the water after you wet your toothbrush.
• Use your dishwasher and clothes washer for only full loads.
• When washing dishes by hand, don't leave the water running for rinsing.
-----x-----X-----x-----