Class X: Chapter 1 (Resources and Development) Question & Answers
Q1. Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Flow
(c) Biotic
(d) Non-renewable
Ans: (d) Non-renewable
Q2. Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put?
(a) Replenishable
(b) Abiotic
(c) Human-made
(d) Non-recyclable
Ans: (a) Replenishable
Q3. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation
(b) Over irrigation
(c) Deforestation
(d) Overgrazing
Ans: (b) Over Irrigation
Q4. In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practiced?
(a) Punjab
(b) Haryana
(c) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(d) Uttarakhand
Ans: (d) Uttarakhand
Q5. In which of the following states is black soil found?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Gujarat
(d) Jharkhand
Ans: (c) Gujarat
Q6. Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
Ans: Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are the three states where black soil is found and cotton is the main crop grown on black soil.
Q7. What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Ans: Alluvial soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast. Three main features of alluvial soil are:
(a) Alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay and is the most fertile soil.
(b) Alluvial soil has adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which is ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat, etc.
(c) According to their age alluvial soil can be classified into two: Old alluvial (Bangar) and new alluvial (Khadar).
Q8. What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Ans: Following steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas:
(a) Terrace Farming: Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terrace. Terrace farming restricts erosion.
(b) Shelter belts: Planting lines of trees to create shelter which will break the force of the wind.
(c) Contour Ploughing: Ploughing along the contour lines can slow down the flow of water down the slopes.
(c) Control over overgrazing.
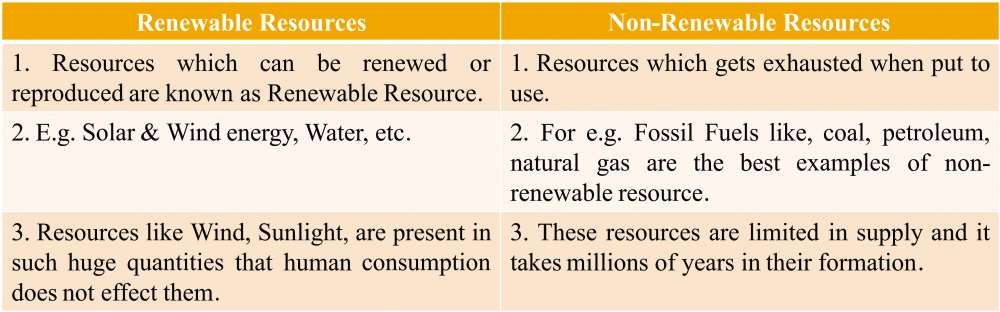
Q9. What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
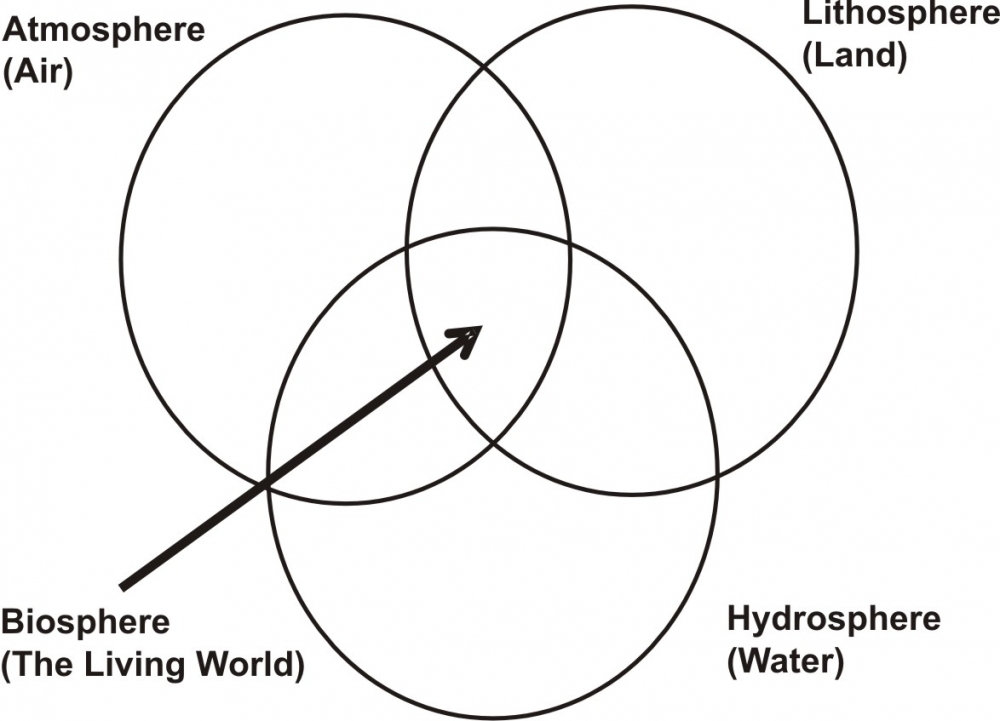
Ans: Biotic Resources: All living things are known as Biotic Resources. These resources are obtained from the Biosphere and they have life. For e.g. Human Beings, Flora, Fauna, fisheries, etc.
Abiotic Resources: All non-living things are known as Abiotic Resources. Resources which are found from the physical or non-living environment. For e.g. Wind, Water, Air, Rocks, Metals, etc.
Q10. Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
Ans: India has total 3.28 million square kilometer. According to the land used data records are available only for about 93% of land of total geographical area. Of the total about 46% of land is used as net sown area, 22% of is forest cover, 5% cultivable land, 8% fallow land, 4% is covered by pastures and 1% is covered by tree crops. The pattern of net sown area varies from state to state. As per National Forest Policy (1952), the forest should be 33% of total geographical area, which is essential to maintain ecological balance but in India the forest cover is only 22%.
Large scale of development, industrialization and urbanization as well as agricultural expansion has widely reduced the forest cover in various parts of the country. Though afforestation and other government policies have lead to a marginal increase in the forest cover area in the country.
Q11. How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Ans: Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development. Technical and economic development always leads to more consumption of all types of resources (i.e. natural and man-made) because of the following reasons:
(a) Technological progress makes available the knowledge to bring resources under use.
(b) With economic progress, more industries will be setup. With growth in industrialization will lead to increasing demand for all the types of resources (i.e. land, labour, capital, etc.).
(c) With technological and economic development income level of the people will increase due to which demands will increase, which will lead to more services and more consumption of resources.
-----x-----X-----x-----




_5_o.jpg)