Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. What is the present average density population of World and India?
Ans: Average density population of the world is 45 persons per sq. km. and India is 364 persons per sq. km.
Q2. Name is least populous continent of the world.
Ans: Antarctica is the least populated continent in the world.
Q3. What do you mean by the age-sex pyramid?
Ans: Age-sex pyramid also known as the Population Pyramid is a graphical representation of the age, sex composition of the population.
Q4. List out the factors responsible for the rapid growth of world population.
Ans: Factors responsible for the rapid growth of world population are:
(a) Geographical Factors: Relief, Climate, Natural Resources, Soil, Water, Minerals.
(b) Social Factors.
(c) Cultural Factors.
(d) Economic Factors.
Q5. Define the following: (a) Birth Rate (b) Death Rate (c) Human Resource.
Ans:
(a) Birth Rate: The number of live births per 1000 persons is called birth rate.
(b) Death Rate: The number of deaths per 1000 persons is called death rate.
(c) Human Resource: Human Resource or people are the greatest asset to a nation. Human beings use their knowledge and skill to convert natural resource into more valuable goods.
Short Answer Questions
Q1. How would you distinguish between productive and dependent population?
Ans:

Q2. Discuss the importance of human resource.
Ans: Human resource or people are a nation's greatest resource; they are an asset to a nation. People are important to develop the economy and society. It is people with their demands and abilities that turn a thing into 'resources'. Human beings use their knowledge and skill to convert natural resource into more valuable goods. Hence, human resource is the ultimate resource. Healthy, educated and motivated people develop resources as per their requirements. Human resources like other resources are not equally distributed over the world.
Long Answer Questions
Q1. Describe the various factors affecting the distribution of population in the world.
Ans: Following are the factors affecting the distribution of population in the world:
Geographical Factors:
(a) Topography: People always prefer to live on plains rather than mountains and plateaus because these areas are suitable for farming, manufacturing and service activities. The Ganga plains are the most densely populated areas of the world while mountains like Andes, Alps and Himalayas are sparsely populated.
(b) Climate: People usually avoid extreme climates that are very hot or very cold like Sahara desert, Polar Regions of Russia, Canada and Antarctica.
(c) Soil: Fertile soils provide suitable land for agriculture. Fertile plains such as Ganga and Brahmaputra in India, Hwang-He, Chang Jiang in China and the Nile in Egypt are densely populated.
(d) Water: People prefer to live in the areas where fresh water is easily available. The river valleys of the world are densely populated while deserts have spare population.
(e) Minerals: Areas with mineral deposits are more populated. Diamond mines of South Africa and discovery of oil in the Middle east lead to settling of people in these areas.
Social, Cultural and Economic Factors:
(a) Social: Areas of better housing, education and health facilities are more densely populated e.g., Pune.
(b) Cultural: Places with religion or cultural significance attract people. Varanasi, Jerusalem and Vatican City are some examples.
(c) Economic: Industrial areas provide employment opportunities. Large number of people are attracted to these areas. Osaka in Japan and Mumbai in India are two densely populated areas.
Q2. Compare the population pyramid of India and Japan. Draw your inferences.
Ans:

Q3. Some regions in India experiencing a steep decline in the sex-ratio. It is unhealthy for the society. Find out reasons and suggest ways to check it.
Ans: Number of female per 1000 male population is called sex ratio. The sex ratio in 2001 was 933 and in 2011 in were 940. Kerala has the best sex ratio (1084); while Sex ration in Gujarat is 919, Haryana (879) and Delhi (868) have the worst sex ratios.
Steep decline in the sex-ratio is a serious threat to the nation. Following are some of the reasons of decline in the sex-ratio:
(a) Girls in India are taken as a liability, one day she will get married and leave the house; Parents have to pay a huge dowry.
(b) Safety and security is a great concern for family.
(c) India is a male dominated country.
(d) Female Feticide, girl child are killed before her birth.
(e) Females often face Malnutrition, leading to ill health.
Steps that can be taken to improve the sex-ratio in India:
(a) People should be educated. Every Indian should change their mindset. Girls are not burden but they are the blessings of the almighty.
(b) Equal rights to male and females.
(c) Female Feticide should be completely banned.
(d) Education for girls.
(e) Nutritious food to be provided.
(f) Every male should respect females in all aspects.
(g) Government of India should take serious steps for the overall development of females.
Q4. China has greater population than India, but has less population density as a whole, while compared to India. Why?
Ans:
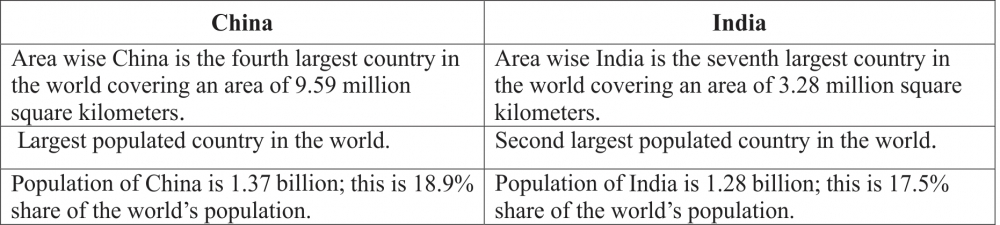
Comparing the data between India and China, area wise China is approximately three times bigger than India, whereas Population wise India's is little less than China, making India more densely populated country than China.
-----x-----X-----x-----

 class ix_0_o.jpg)








