Happy Basant Panchami, Jai Mata Di


Q1. What is density of population? Give India's population distribution by density with the reasons responsible for the same.
Q2. What are the advantages of a healthy population?
Q3. What is the role of NPP 2000 in the life of adolescent?
Q4. What is the relationship between occupational structure and development?
Q5. What are the major components of population growth?
Q6. Which areas are sparsely populated in India and why?
Q7. What significant improvements have been noticed in the health status of our population?
Q8. What is age composition? How does it affect the population's social and economic structure?
Q9. What does the national population policy indicates?
Q10. Explain the following:
(a) Sex ratio in India
(b) Literacy rate in India
(c) Population size and figure of India
Q11. Map skills
(a) Densely populated state of India
(b) Less populated state of India
(c) The state of highest density of population
(d) The state of lowest density of population
(e) The state of highest literacy rate
(f) The state of lowest literacy rate
(g) The state of highest sex ratio
(h) The state of lowest sex ratio
(i) Union territory of lowest sex ratio
Q1. Why is the rate of population growth in India declining since 1981?
Ans: The rate of population growth in India is declining since 1981 because:
(a) The family planning programme initiated by the government made a great impact on the mindset of the people.
(b) Educational programmes have improved the literacy rate helping in increasing the awareness about the benefits of smaller family size.
(c) Parents became aware and wanted to give better quality of life to their children, i.e. good education, food, clothing, health, etc
Q2. Discuss the major components of population growth.
Ans: Major components of population growth are:
(a) Birth rate
(b) Death rate
(c) Migration
A higher birth rate, with a lower death rate leads to population growth. International migration can lead to population growth.
Q3. Define age structure, death rate and birth rate.
Ans: Age Structure: Number of people in different age groups in country is called age structure of the population. Population of a nation is generally grouped into three broad categories:
(a) Children (Below 15 years of age): Economically unproductive and needs to be provided with the necessities of life (food, cloth, education, etc.)
(b) Working age (15 – 59 years): Economically and biologically productive
(c) Aged (Above 59 years of age): They can be economically productive even after retirement.
Death Rate: The number of deaths per 1000 persons is called death rate.
Birth Rate: The number of live births per 1000 persons is called birth rate.
Q4. How is migration a determinant factor of population change?
Ans: Movement of people from one place to another; in search of livelihood is called migration. Migration can be classified into two:
(a) Migration within the country is called internal migration.
(b) Migration between two countries is called international migration.
Internal migration has no change on population size but it changes the population composition of a particular area. International migration can lead to a growth or degrowth in population; depending on the degree of immigration and emigration.
In India, Poverty and lack of employment opportunities in rural areas work as 'push' factors which result in migration to urban areas. Better employment opportunities in urban areas work as 'pull' factors for migration. Due to increased migration towards urban areas, the share of urban population has increased from 17.29% in 1951 to 27.78% in 2001.
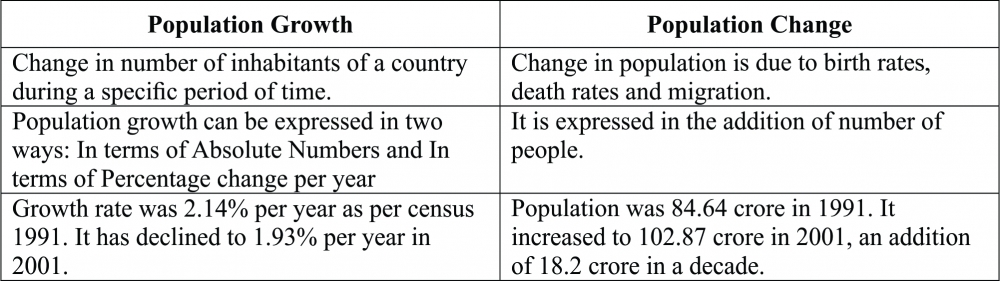
Q5. Distinguish between population growth and population change.
Ans:
Q6. What is the relation between occupational structure and development?
Ans: Occupational structure has got a great impact on the development of any country. In India more than 60% of the population is engaged in the agricultural activities and thus, are still dependent on the primary sector for employment, which is one of the reasons for lack of development in India. The developed nations suggest that when a greater portion of population engages in secondary and tertiary activities, it leads to great development.
Q7. What are the advantages of having a healthy population?
Ans: It is rightly said, a healthy mind resides in a healthy body. Human resource is the most important resource for the development of a country. A healthy population helps in building a productive workforce for the country. If the health of the population is properly looked after, people can put in more number of working hours and thus, the production level of the country can be increased. Even the non-productive age group needs to be healthy to reduce the burden of healthcare. Healthy children would grow into healthy adults and would be able to contribute better in the economy. Healthy elders would mean less drain on the resources.
Q8. What are the significant features of the National Population Policy 2000?
Ans: The new national population policy of 2000 was announced by the Government of India, its main features are:
(a) Redress the unmet needs for basic reproductive and child health services, supplies and infrastructure.
(b) Free and compulsory school education up to age 14, for both boys and girls.
(c) Reduce infant mortality rate to below 30 per 1000 live births.
(d) Reduce maternal mortality ratio to below 100 per 100,000 live births.
(e) Achieve universal immunization of children against all vaccine preventable diseases.
(f) Promote delayed marriage for girls, not earlier than age 18 and preferably after 20 years of age.
(g) Achieve 80 per cent institutional deliveries and 100 percent deliveries by trained persons.
(h) Making family welfare a people centered programme.
(i) Preventing and controlling transmissible diseases.
-----x-----X-----x-----

Human beings depended entirely on nature for food, clothing and shelter; but with time they learnt new skills to grow food, build homes and develop better means of transport and communication. In this way they modified the environment where they lived.
Settlement:
1. Earlier man lived a nomadic life, moving from one place to another in search of food and shelter, later man invented agriculture and started leading a more settled life.
2. The settlements grew near the river valleys as water was available and land was fertile. With the development of trade, commerce and manufacturing, human settlements became larger.
What is settlement?
Ans: It is a place where people build their homes and interact with each other, carrying out various occupational activities which help making life more comfortable.
TYPES OF SETTLEMENTS

Settlements can be classified into two types: - Temporary or Permanent Settlements

Permanent Settlements can be classified into two types: - Rural and Urban settlements

Rural Settlements can be classified into two types: - Isolated and Compact Settlements

TRANSPORT
Transport is the means by which people and goods move from one place to another.In the early days it took a great deal of time, to travel long distances. People had to walk and used animals to carry their goods.Invention of the wheel made transport easier. With the passage of time different means of transport developed to a great extent.
MEANS OF TRANSPORTATION


ROADWAYS
RAILWAYS
WATERWAYS

AIRWAYS

COMMUNICATION
-----x-----X-----x-----
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. What do you mean by natural vegetations?
Ans: Plants which grow naturally without any human interference, covering a large area is known as natural vegetation.
Q2. Name the factors on which growth of vegetation depends.
Ans: Rainfall, Temperature, Relief, Soil & its fertility, height above sea level, Sunshine, Drainage, etc.
Q3. Why are the trees in Evergreen forests remain green all round the year?
Ans: In the Evergreen forests there is no particular dry season, the trees do not shed their leaves altogether. Thus, these forests remain green all round the year.
Q4. What makes Camel an essential animal for the desert dwellers?
Ans: Camel is the most important animal of the deserts also known as the Ship of the desert. Camels have special body features which help them to survive in extreme conditions. Camels can survive for many days without water.
Q5. Why are several plants, animals and birds becoming endangered species?
Ans: Human activities like deforestation, agriculture, mining, hunting, industrialization, modernization, etc. have destroyed several ecosystems to meet their demands, making several plants, animals and birds becoming endangered species.
Short Answer Questions
Q6. Distinguish between (i) Evergreen and Deciduous Forests (ii) Tropical and Temperate Grasslands
Ans.
(i) Evergreen and Deciduous Forests

(ii) Tropical and Temperate Grasslands

Q7. Why do softwood trees have great commercial value?
Ans. Softwood trees have great commercial value because the wood is used for manufacturing paper and newsprint. The wood is also used for making furniture, matchstick, plywood and sports goods. Infact, 80% of the world timber comes from softwood trees.
Q8. How do shrubs and some trees survive in hot deserts?
Ans. Shrubs and trees found in the hot deserts have some special characteristics. Vegetation cover includes thorny bushes, cacti and few short trees. These have long roots, thick stems, waxy leaves and thorns which help the vegetation to survive in such harsh climatic conditions.
Q9. Why is there very limited vegetation in the Ladakh region?
Ans. Ladakh region is like a cold desert, there is snow cover through the year. The extremely cold conditions do not allow the growth of vegetation on a large scale. Thus, we find very limited vegetation in these regions.
Long Answer Questions
Q10. Describe the main characteristics of tropical rain forests.
Ans. Characteristics of the tropical rain forests are as follows:
(a) These regions are hot and receive heavy rainfall throughout the year.
(b) As there is no particular dry season, the trees do not shed their leaves altogether. This is the reason they are called evergreen.
(c) Maximum varieties of trees are found. Trees are tall with large trunks.
(d) The thick canopies of the closely spaced trees do not allow the sunlight to penetrate inside the forest even in the day time. Thus, grass is not found in these forests.
(e) Hardwood trees like rosewood, teak, sal, ebony, and mahogany are the common trees found here.
(f) Here the population found is very less. Due to dense forests commercial exploitation of these forests has not be possible, making them economically backward.
(g) Large variety and most colourful animals are found here.
(h) Monkey, Ape, Birds, Hippopotamus, snake, python, Frog, Crocodile, etc. Anaconda, world's largest snake is also found in these areas.
Q11. Where are Mediterranean forests located? Highlight the main characteristics of the trees found here.
Ans. Mediterranean forests are found on the western margins of continents in the warm temperate regions, in areas around Mediterranean Sea, Central Chile, South-West USA, Australia, Africa.
Some of the main characteristics of the trees found here are:
(a) Mediterranean trees adapt themselves to dry summers with the help of their thick barks and wax coated leaves which help them reduce transpiration. Also, here the plants have long tap roots to reach underground water, called "Xerophytic Plants".
(b) Mediterranean regions are known as 'Orchards of the world' for their fruit cultivation.
(c) Citrus fruits such as oranges, figs, olives and grapes are commonly cultivated here because people have removed the natural vegetation in order to cultivate what they want to.
Q12. Why do the trees in the Coniferous forests have conical shape?
Ans. Chir, pine, cedar, etc. are the important variety of trees found in these forests. These trees are tall, straight and conical shaped with needle shaped leaves. The conical shapes of these trees are best suited to the climatic conditions as it allows the snow to slide down the leaves and branches of these trees.
-----x-----X-----x-----