Class VIII: Chapter 5 (Industries)
There are three types of economic activities. These are:
1. Primary Activities: Connected with extraction and production of natural resources like forestry, agriculture, mining, animal husbandry, etc.
2. Secondary Activities: Connected with processing and manufacturing. They get raw material from the Primary sector. When the primary product is processed into a secondary product, its utility and value is increased.
3. Tertiary Activities: Provides support to Primary and Secondary sectors through services, e.g. transportation, banking, tourism, etc.
MANUFACTURING: Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw material to more valuable products is called "Manufacturing".
INDUSTRY: Industry refers to an economic activity that is concerned with the production of goods, extraction of minerals or the provision of services.
THE ECONOMIC STRENGTH OF A COUNTRY IS MEASURED BY THE DEVELOPMENT OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIES.
Q. Why manufacturing sector is considered as the economic backbone of a country?
Ans: -
- Industrial growth helps in modernising the agricultural activities by providing machinery, chemicals, irrigation facilities, insecticides, pesticides, etc.
- Industrial growth helps in reducing the unemployment and poverty.
- Industrial growth can earn foreign exchange by exporting the finished goods and thus, can expand its trade and commerce.
INDUSTRIAL LOCATION
Factors effecting the location of an Industry are: -
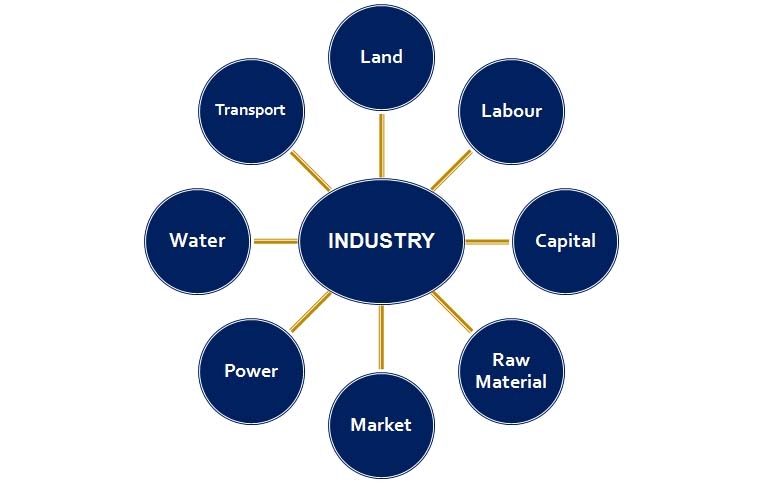
- Industrialization leads to urbanization.
- Government policies also play a key factor in deciding the location of an industry. The government provides incentives like subsidised power, lower transport cost and other infrastructure

INDUSTRIAL SYSTEM
An industrial system consists of inputs, processes and outputs.
Input: Raw materials, labour, costs of land, transport, power and other infrastructure.
Process: All activities that convert the raw material into finished products.
Output: End/ Final/Finished product and the income earned from it.

INDUSTRIAL REGIONS
- The region where a number of industries locate close to each other and share the benefits of their closeness can be termed as Industrial regions.
- Major industrial regions tend to be located in the temperate areas, near sea ports and especially near coal fields.
Industrial Regions of the World are: -
1. Great Lakes Industrial Region of North America.
2. Rhur-Saar Industrial Region of Europe.
3. London Industrial Region.
4. Ural-Ukraine Industrial Region of Russia.
5. Sydney Industrial Region of Australia.
Major industrial regions in India are: -
1. Mumbai-Pune cluster
2. Bangalore-Tamil Nadu region
3. Hugli region
4. Ahmedabad-Baroda region
5. Chottanagpur industrial belt
6. Vishakhapatnam-Guntur belt
7. Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut region
8. Kollam-Thiruvanathapuram industrial cluster.
CLASSIFICATION OF INDUSTRIES

1. On the basis of Raw Materials: These types of industries are classified depending on the type of raw materials they use.
(a) Agro Based Industries: Use plant and animal based products as their raw materials. E.g. Food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile, dairy products, etc.
(b) Mineral Based Industries: Primary industries that use mineral ores as their raw materials. The products of these industries feed other industries. Iron made from iron ore is the product of mineral based industry. E.g. Iron& Steel, Cement, Machine Tools, etc.
(c) Marine Based Industries: Use products from the sea and oceans as raw materials. E.g. processed sea food, fish oil manufacturers, etc.
(d) Forest Based Industries: Use forest produce as raw materials. E.g. pulp & paper, furniture. Pharmaceuticals, etc.
2. On the basis of Size: These types of industries are classified depending on the amount of capital invested, number of people employed and the volume of production.
(a) Large Scale Industries: In India, on an industry, if the capital invested is more than 1 crore, then it is called Large Scale Industry. E.g. Iron & Steel Industries, Automobile Industries, etc.
(b) Small Scale Industries: In India, on an industry, if the capital invested is less than 1 crore, then it is called Small Scale Industry. E.g. Silk weaving, Food processing industries, etc.
Cottage or household industries are a type of small scale industry where the products are manufactured by hand, by the artisans with the help of family members. E.g. Basket weaving, pottery, handicrafts, etc.
3. On the basis of Ownership: These types of industries are classified on the basis of ownership.
(a) Private Sector Industries: Owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals. E.g. Bajaj Auto, Reliance, etc.
(b) Public Sector Industries: Owned and operated by the government. E.g. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Bharat Heavy Electronics Ltd. (BHEL), SAIL, etc.
(c) Joint Sector Industries: Owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. Maruti Udyog Limited. E.g. processed sea food, fish oil manufacturers, etc.
(d) Co-operative Sector Industries: Owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both. E.g. IFFCO, Anand Milk Union Limited (AMUL) and Sudha Dairy, etc.
INDUSTRIAL DISASTER
In industries, accidents/disasters mainly occur due to technical failure or irresponsible handling of hazardous material.
One of the worst industrial disasters of all time occurred in Bhopal on 3 December 1984 around 00:30 a.m. It was a technological accident in which highly poisonous Methyl Isocynate (MIC) gas along with Hydrogen Cyanide and other reaction products leaked out of the pesticide factory of Union Carbide. The official death toll was 3,598 in 1989. Thousands, who survived still suffer from one or many ailments like blindness, impaired immune system, gastrointestinal disorders etc.
Mitigation Strategies
1. Densely populated residential areas should be separated far away from the industrial areas.
2. People staying in the vicinity of industries should be aware of the storage of toxins or hazardous substances and their possible effects in case if an accident occurs.
3. Fire warning and fighting system should be improved.
4. Storage capacity of toxic substances should be limited.
5. Pollution dispersion qualities in the industries should be improved.
DISTRIBUTION OF MAJOR INDUSTRIES
The world's three major industries are:
1. Iron & Steel Industry
2. Textile Industry
3. Information Technology Industry
The iron & steel and textile industry are the older industries while information technology is an emerging industry.
EMERGING INDUSTRIES ARE ALSO KNOWN AS 'SUNRISE INDUSTRIES'
IRON & STEEL INDUSTRY:
- This is basic industry.
- These industries are the feeder industry whose products are used as raw material for other industries.
- Inputs: Raw materials such as iron ore, coal and limestone, along with labour, capital, site and other infrastructure.
- Process: Converting iron ore into steel involves many stages. The raw material is put in the blast furnace where it undergoes smelting and then it is refined.
- Output: Steel is obtained which is used by other industries as raw material.
- Steel is often called the backbone of modern industry.
- Almost everything we use is either made of iron or steel or has been made with tools and machinery of these metals. From safety pin to Ships, trains, trucks, and autos are made largely of steel.
- Before 1800 A.D. iron and steel industry was located where raw materials, power supply and running water were easily available.
- Later the ideal location for the industry was near coal fields and close to canals and railways.
- After 1950, iron and steel industry began to be located on large areas of flat land near sea ports.
- India, Germany, USA, China, Japan, Russia, Korea, etc. are the countries, where steel industries are located.
- In India important steel producing centres are: Bhilai, Durgapur, Burnpur, Jamshedpur, Rourkela, Bokaro are situated in a region that spreads over four states — West Bengal, Jharkhand, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
- Bhadravati and Vijay Nagar in Karnataka, Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, Salem in Tamil Nadu are other important steel centres utilising local resources.
- India's steel production increased from one million tonne in 1947 to 30 million tonnes in 2002.
Tata Iron and Steel Industry in Jamshedpur:
- Before 1947, there was only one iron and steel plant in the country – Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited (TISCO).
- It was privately owned.
- TISCO was started in 1907 by Jamshedji N. Tata at Sakchi in the Singhbhum district of Jharkhand, but the production started in 1910. Later on Sakchi was renamed as Jamshedpur.
Sakchi was chosen to set up the steel plant because of the following reasons: -
1. This place was only 32 km away from Kalimati station on the Bengal-Nagpur railway line.
2. It was close to the iron ore, coal and manganese deposits as well as to Kolkata, which provided a large market.
3. TISCO gets coal from Jharia coalfields, and iron ore, limestone, dolomite and manganese from Orissa and Chhattisgarh.
4. The Kharkai and Subarnarekha rivers ensured sufficient water supply.
5. Government initiatives provided adequate capital for its later development. This lead to rapid industrial growth in India.
Iron and Steel Industry at Pittsburgh (USA):
- It is an important steel city of the United States of America. Pittsburgh is also known as "Iron City"
- In mid 19th century processing of Iron began in Pittsburgh.
- The steel industry at Pittsburgh enjoys locational advantages. Some of the raw material such as coal is available locally, while the iron ore comes from the iron mines at Minnesota, about 1500 km from Pittsburgh. Between these mines and Pittsburgh is one of the world's best routes for shipping ore cheaply – the famous Great Lakes waterway. Trains carry the ore from the Great Lakes to the Pittsburgh area. The Ohio, the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers provide adequate water supply.
- The Geographical conditions of Pittsburgh have a favourable topography, temperate climate, skilled labour and market, which make this place favourable for the development of Iron & Steel industry.
TEXTILE INDUSTRY:
- Weaving cloth from yarn is an ancient art and it is done on looms. Hand operated looms are called Handlooms and power operated looms are called Powerlooms.
- Cotton, wool, silk, jute, flax have been used for making cloth.
- The textile industry can be divided on the basis of raw materials used in them.
- Fibres are the raw material of textile industry. Fibres can be natural or man-made. Natural fibres are obtained from wool, silk, cotton, linen and jute. Manmade fibres include nylon, polyester, acrylic and rayon.
- The cotton textile industry is one of the oldest industries in the world.
- India has a glorious tradition of producing excellent quality cotton textiles. Before the British rule, Indian hand spun and hand woven cloth already had a wide market. The Muslins of Dhaka, Chintzes of Masulipatnam, Calicos of Calicut and Gold-wrought cotton of Burhanpur, Surat and Vadodara were known worldwide for their quality and design. But the production of hand woven cotton textile was expensive and time consuming. Hence, traditional cotton textile industry could not face the competition from the new textile mills of the West, which produced cheap and good quality fabrics through mechanized industrial units.
- The first successful mechanized textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
- The warm, moist climate, a port for importing machinery, availability of raw material and skilled labour resulted in rapid expansion of the industry in the region.
- Initially this industry flourished in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat because of favourable humid climate.
- Today, Coimbatore, Kanpur, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Mumbai, Kolkata, Ludhiana, Pondicherry and Panipat are some of the other important centres.
Ahmedabad:
- It is located in Gujarat on the banks of the Sabarmati River.
- The first mill was established in 1859. It soon became the second largest textile city of India, after Mumbai.
- Ahmedabad was therefore often referred to as the 'Manchester of India'.
- Favourable locational factors were responsible for the development of the textile industry in Ahmedabad.
- Ahmedabad is situated very close to cotton growing area. This ensures easy availability of raw material.
- The climate is ideal for spinning and weaving.
- The flat terrain and easy availability of land is suitable for the establishment of the mills.
- The densely populated states of Gujarat and Maharashtra provide both skilled and semi-skilled labour.
- Well developed road and railway network permits easy transportation of textiles to different parts of the country, thus providing easy access to the market. Mumbai and Kandla ports nearby facilitates import of machinery and export of cotton textiles.
Osaka:
- It is an important textile centre of Japan, also known as the 'Manchester of Japan'.
- The extensive plain around Osaka ensured that land was easily available for the growth of cotton mills. Warm humid climate is well suited to spinning and weaving.
- The river Yodo provides sufficient water for the mills.
- Labour is easily available.
- Location of port facilitates import of raw cotton and for exporting textiles.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT):
- Today, IT industry has become global and has become the fastest growing industry in the world.
- The information technology industry deals in the storage, processing and distribution of information through Radio, Television, Telephones, Cellular Phones, Computers, Laptops, etc.
- Availability of resources, cost and infrastructure are the main factors responsible for the location of an IT industry.
- The major hubs of the IT industry are the Silicon Valley and Bangaluru in India.
Silicon Valley (California, USA):
- Silicon Valley is a part of Santa Clara Valley, located on the San Francisco-California Peninsular in the USA.
- Temperate climate is favourable for the industry.
- Availability of skilled labour and market has played an important role in the grown of IT industry.
Bangaluru (Karnataka, India):
- Bangalore is located on the Deccan Plateau from where it gets the name 'Silicon Plateau'.
- The city is known for its mild climate throughout the year. Pleasant weather, low cost of living, makes it an ideal place for living.
- Good transport facility, availability of skilled and experienced professionals.
- More than 100 multinational and software companies have established their business.
- Other emerging information technology hubs in metropolitan centres of India such as Mumbai, New Delhi, Hyderabad and Chennai, Gurgaon, Pune, Thiruvanthapuram, Kochi and Chandigarh, etc.
-----x-----X-----x-----




 map work_1_o.jpg)