Pre-Summative – II (Social Science, Class – IX)
Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
General Instructions:
The question paper has 30 questions in all.
All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated against each question.
I. Questions from serial number 1 to 8 carry one mark each.
II. Questions from serial number 9 to 20 are 3 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 80 words each.
III. Questions from serial number 21 to 28 are 5 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 120 words each.
IV. Question number 29 and 30 are map questions of 3 marks each from History and Geography respectively. After completion, attach the map inside your answer book.
***************************************************************************************************************
Q1.What was the main object of National Assembly in France while drafting the constitution in 1791?
Q2. Which drainage pattern is formed by River Ganga?
Q3 .Which is the western most longitude of India?
Q4. Name the part of Himalaya lying between Kali and Tista rivers.
Q5. Pinochet rule in Chile ended after he decided to hold a referendum. In which year was referendum held?
Q6. When did Mexico get independence?
Q7.How much time did it take the Constituent Assembly to complete the Indian Constitution?
Q8 .What was the expenditure percentage of GDP in 1951-52 on education?
Q9. Describe the events of 14th July 1789.
Q10 (a) Who were radicals? Describe briefly.
OR
10 (b) Explain the new education policy introduced by Hitler in Germany.
Q11 (a) Explain any three differences between the political ideas of Liberals and Radicals in Russia during the early twentieth century.
OR
11(b) Highlight three main features of the Nazi World view?
Q12. India accounts for about 2.4 percent of the total geographical area of the world but supports the second largest population of the world. What are its three implications?
Q13. Justify the naming of Indian Ocean after India.
Q14. Mention any six tectonics plates of the earth's crust.
Q15. Name the three sections into which Northern plain has been divided. Write one feature of each.
Q16. How did Robert Mugabe's party ZANU PF violate the features of a democratically elected government? Mention any three methods adopted by the party.
Q17. ‟The Constituent Assembly worked in a systematic open and consensual manner." Mention any three values that are depicted by the Constituent Assembly.
Q18. Describe any three demands of the workers of "Lenin Shipyard" during their strike which started in August 1980 in Poland.
Q19. Describe any three ways by which production can be increased from a fixed plot of land.
Q20. What does a "virtuous cycle" created by the educated parents mean? Explain.
Q21. Explain the immediate causes of the outbreak of the revolt in France in 1789.
Q22 (a) Explain any five socio – economic conditions of Russia at the beginning of the twentieth century?
OR
22 (b) Hitler's foreign policy aimed at gaining power and prestige for Germany. State this features of his foreign policy.
Q23. Give an account of the four divisions of Himalayas from west to east along with Purvanchal hills respectively.
Q24. Even democracy has a fair share of demerits. Point out five such demerits.
Q25. Highlight the salient features of the Constitution of India.
Q26. Explain the meaning of "Physical Capital"? Explain its two types with the help of suitable examples.
Q27. Explain any five effects of unemployment in India.
Q28. "Green Revolution is associated with loss of soil fertility". In the light of the statement mention five problems caused by modern farming.
Q29. Three items A, B and C are shown in the given outline map of France. Identify these items with the help of following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
(A) Port related to slave trade.
(B) The region not affected by the great fear.
(C) The place where French revolution of 1789 started.

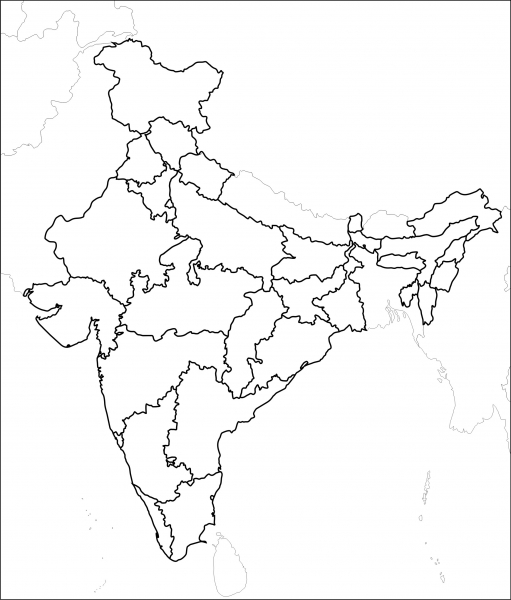
Q30. On the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols:
(X) Standard Meridian of India
(Y) Jaintia Hills
(Z) River Tapi
-----x-----X-----x-----

_0_o.jpg)

 map work_0_o.jpg)